Mudanças entre as edições de "Teste"
| Linha 82: | Linha 82: | ||
*'''Prefetch: <yes or no / sim ou não>''' | *'''Prefetch: <yes or no / sim ou não>''' | ||
**If yes, message cache elements are prefetched before they expire to keep the cache up to date. Default is no. Turning it on gives about 10 percent more traffic and load on the machine, but popular items do not expire from the cache. | **If yes, message cache elements are prefetched before they expire to keep the cache up to date. Default is no. Turning it on gives about 10 percent more traffic and load on the machine, but popular items do not expire from the cache. | ||
| − | **'''Tradução: '''Se sim, elementos de cache mensagem são previamente antes que expirem para manter o cache atualizado. O padrão é não. Ligá-lo dá cerca de 10 por cento mais tráfego e carga na máquina , mas itens populares não expiram a partir do cache. | + | **'''Tradução: '''Se sim, elementos de cache mensagem são previamente buscados antes que expirem para manter o cache atualizado. O padrão é não. Ligá-lo dá cerca de 10 por cento mais tráfego e carga na máquina , mas itens populares não expiram a partir do cache. |
*'''Prefetch Key: <yes or no / sim ou não>''' | *'''Prefetch Key: <yes or no / sim ou não>''' | ||
| − | **If yes, fetch the DNSKEYs earlier in the validation process, when a DS record is encountered. This lowers the latency of requests. It does use a little more CPU. | + | **If yes, fetch the DNSKEYs earlier in the validation process, when a DS record is encountered. This lowers the latency of requests. It does use a little more CPU. |
| − | **'''Tradução: '''Se sim, | + | **'''Tradução: '''Se sim, busca os DNSKEYs no início do processo de validação, quando um registro DS é encontrado. Isso diminui a latência de pedidos . Ele usa um pouco mais CPU. |
Edição das 15h52min de 16 de agosto de 2016
PAGINA DE TESTES
Config
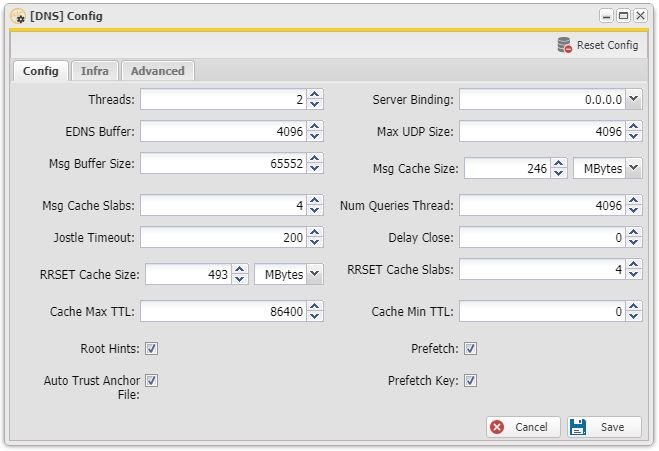
- Threads: <number / número>
- The number of threads to create to serve clients. Use 1 for no threading.
- Tradução: O número de threads criadas para atender os clientes . Use 1 para nenhuma threads.
- EDNS Buffer: <number / número>
- Number of bytes size to advertise as the EDNS reassembly buffer size. This is the value put into datagrams over UDP towards peers. The actual buffer size is determined by msg-buffer-size (both for TCP and UDP). Do not set higher than that value. Default is 4096 which is RFC recommended. If you have fragmentation reassembly problems, usually seen as timeouts, then a value of 1480 can fix it. Setting to 512 bypasses even the most stringent path MTU problems, but is seen as extreme, since the amount of TCP fallback generated is excessive (probably also for this resolver, consider tuning the outgoing tcp number).
- Tradução: Número de bytes para anunciar que o tamanho do buffer de remontagem EDNS . Este é o valor colocado em datagramas sobre UDP no sentido de pares. O tamanho do buffer real é determinada por msg-buffer-size ( tanto para TCP e UDP). Não ajuste maior do que esse valor. O padrão é 4096 , que é recomendado RFC . Se você tem problemas de fragmentação remontagem, geralmente vistos como tempos de espera , em seguida, um valor de 1480 pode corrigi-lo . Definir a 512 ignora até mesmo o caminho mais rigorosas problemas MTU , mas é visto como extremo, uma vez que a quantidade de retorno TCP gerado é excessivo (provavelmente também para este resolver, considere ajustar o número de TCP de saída) .
- Msg Buffer Size: <number / número>
- Number of bytes size of the message buffers. Default is 65552 bytes, enough for 64 Kb packets, the maximum DNS message size. No message larger than this can be sent or received. Can be reduced to use less memory, but some requests for DNS data, such as for huge resource records, will result in a SERVFAIL reply to the client.
- Tradução: Número de bytes dos buffers de mensagens . O padrão é 65552 bytes , o suficiente para pacotes de 64 kb , o tamanho máximo da mensagem DNS. Nenhuma mensagem maior do que este pode ser enviado ou recebido. Pode ser reduzido para usar menos memória , mas alguns pedidos de dados de DNS, como para grandes registros de recursos , irá resultar em uma resposta SERVFAIL para o cliente.
- Msg Cache Slabs: <number / número>
- Number of slabs in the message cache. Slabs reduce lock contention by threads. Must be set to a power of 2. Setting (close) to the number of cpus is a reasonable guess.
- Tradução: Número de lajes no cache de mensagem. Lajes reduzir a contenção de bloqueio por threads. Deve ser definido como uma potência de 2. Setando (fechar) para o número de CPUs é uma suposição razoável .
- Jostle Timeout: <msec / millessegundos>
- Timeout used when the server is very busy. Set to a value that usually results in one roundtrip to the authority servers. If too many queries arrive, then 50% of the queries are allowed to run to completion, and the other 50% are replaced with the new incoming query if they have already spent more than their allowed time. This protects against denial of service by slow queries or high query rates. Default 200 milliseconds.
- Tradução: Tempo esgotado usado quando o servidor está muito ocupado. Definido para um valor que geralmente resulta em uma ida e volta para os servidores de autoridade. Se muitas consultas chegar, em seguida, 50% das consultas estão autorizados a executar para conclusão , e os outros 50 % são substituídos com a nova consulta de entrada , se já tiverem passado mais de seu tempo permitido. Isso protege contra a negação de serviço por consultas lentas ou taxas de consulta elevados. Padrão 200 milissegundos .
- RRSET Cache Size: <number / número>
- Number of bytes size of the RRset cache. Default is 4 megabytes. A plain number is in bytes, append 'k', 'm' or 'g' for kilobytes, megabytes or gigabytes (1024*1024 bytes in a megabyte).
- Tradução: Número de bytes do cache RRSET . O padrão é 4 megabytes. Um número simples está em bytes , acrescentar 'k' , 'm' ou 'g' para kilobytes, megabytes ou gigabytes (1024 * 1024 bytes em um megabyte ) .
- Cache Max TTL: <seconds / segundos>
- Time to live maximum for RRsets and messages in the cache. Default is 86400 seconds (1 day). If the maximum kicks in, responses to clients still get decrementing TTLs based on the original (larger) values. When the internal TTL expires, the cache item has expired. Can be set lower to force the resolver to query for data often, and not trust (very large) TTL values.
- Tradução: Tempo de vida máximo para RRsets e mensagens no cache. O padrão é 86400 segundos (1 dia) . Se os pontapés máximas em, respostas para os clientes ainda obter decremento TTLs com base nos valores originais (maiores) . Quando o TTL interna expirar, o item de cache expirou. Pode ser definido mais baixo para forçar a resolver a consulta para dados, muitas vezes , e não confiar (muito grande ) valores TTL .
- Max UDP Size: <number / número>
- Maximum UDP response size (not applied to TCP response). 65536 disables the udp response size maximum, and uses the choice from the client, always. Suggested values are 512 to 4096. Default is 4096.
- Tradução: O tamanho máximo da resposta UDP ( não aplicado a resposta TCP ) . 65536 desativa o tamanho máximo de resposta UDP , e usa a escolha do cliente , sempre. Os valores sugeridos são 512 para 4096. O padrão é 4096 .
- Msg Cache Size: <number / número>
- Number of bytes size of the message cache. Default is 4 megabytes. A plain number is in bytes, append 'k', 'm' or 'g' for kilobytes, megabytes or gigabytes (1024*1024 bytes in a megabyte).
- Tradução: Número de bytes do cache de mensagem . O padrão é 4 megabytes. Um número simples está em bytes , acrescentar 'k' , 'm' ou 'g' para kilobytes, megabytes ou gigabytes (1024 * 1024 bytes em um megabyte ) .
- Num Queries Thread: <number / número>
- The number of queries that every thread will service simultaneously. If more queries arrive that need servicing, and no queries can be jostled out (see jostle-timeout), then the queries are dropped. This forces the client to resend after a timeout; allowing the server time to work on the existing queries. Default depends on compile options, 512 or 1024.
- Tradução: O número de consultas que cada tarefa irá servir simultaneamente. Se mais consultas chegar a essa necessidade de manutenção, e sem consultas podem ser empurrado para fora ( veja jostle-timeout ) , em seguida, as consultas são descartados . Isso força o cliente para reenviar após um tempo limite ; permitindo que o horário do servidor para trabalhar nas consultas existentes . O padrão depende opções de compilação , 512 ou 1024.
- Delay Close: <msec / milissegundos>
- Extra delay for timeouted UDP ports before they are closed, in msec. Default is 0, and that disables it. This prevents very delayed answer packets from the upstream (recursive) servers from bouncing against closed ports and setting off all sort of close-port counters, with eg. 1500 msec. When timeouts happen you need extra sockets, it checks the ID and remote IP of packets, and unwanted packets are added to the unwanted packet counter.
- Tradução: Atraso extra do tempo esgotado para portas UDP antes de serem fechados, em milissegundos. O padrão é 0, e que desativa. Isso impede que muito atraso pacotes de resposta dos servidores a montante ( recursivo) de saltar contra portas fechadas e desencadeando todo o tipo de contadores porta fechada , como por exemplo 1500 ms. Quando os tempos de espera acontecer você precisa soquetes extras , ele verifica o ID e IP remoto de pacotes e pacotes indesejados são adicionados ao contador de pacotes indesejados.
- RRSET Cache Slabs: <number / número>
- Number of slabs in the RRset cache. Slabs reduce lock contention by threads. Must be set to a power of 2.
- Tradução: Número de lajes no cache RRSET . Lajes reduzir a contenção de bloqueio por tarafas. Deve ser definido como uma potência de 2 .
- Cache Min TTL: <seconds>
- Time to live minimum for RRsets and messages in the cache. Default is 0. If the minimum kicks in, the data is cached for longer than the domain owner intended, and thus less queries are made to look up the data. Zero makes sure the data in the cache is as the domain owner intended, higher values, especially more than an hour or so, can lead to trouble as the data in the cache does not match up with the actual data any more.
- Tradução: Tempo de vida mínimo para RRsets e mensagens no cache. O padrão é 0. Se os pontapés mínimos , os dados são armazenados em cache por mais tempo que o proprietário do domínio pretendido, e, portanto, menos consultas são feitas para olhar para cima os dados. Zero garante que os dados no cache é como o proprietário do domínio pretendido , os valores mais elevados , especialmente mais de uma hora ou mais, pode levar a problemas como os dados no cache não corresponder-se com os dados reais.
- Root Hints: <yes or no / sim ou não>
- Read the root hints from this file. Default is nothing, using builtin hints for the IN class. The file has the format of zone files, with root nameserver names and addresses only. The default may become outdated, when servers change, therefore it is good practice to use a root-hints file.
- Tradução: Leia as dicas de raiz a partir deste arquivo . O padrão é nada , usando sugestões embutidas para a classe IN. O arquivo tem o formato de arquivos de zona , com nomes de servidores de nomes de raiz e endereços únicos . O padrão pode tornar-se desatualizado, quando os servidores mudam, portanto, é uma boa prática para usar um arquivo de root- dicas.
- Auto Trust Anchor File: <yes or no / sim ou não>
- File with trust anchor for one zone, which is tracked with RFC5011 probes. The probes are several times per month, thus the machine must be online frequently. The initial file can be one with contents as described in trust-anchor-file. The file is written to when the anchor is updated, so the unbound user must have write permission. Write permission to the file, but also to the directory it is in (to create a temporary file, which is necessary to deal with filesystem full events).
- Tradução: Arquivo com âncora de confiança para uma zona , que é rastreada com sondas RFC5011 . As sondas são várias vezes por mês , assim, a máquina deve ser on-line com frequência. O arquivo inicial pode ser um com conteúdos como descrito na confiança - arquivo - âncora - . O arquivo é gravado quando a âncora é atualizado, para que o usuário não ligado deve ter permissão de gravação . Escrever permissão para o arquivo, mas também para o diretório é no ( para criar um arquivo temporário , que é necessário para lidar com eventos completos de sistema de arquivos ) .
- Prefetch: <yes or no / sim ou não>
- If yes, message cache elements are prefetched before they expire to keep the cache up to date. Default is no. Turning it on gives about 10 percent more traffic and load on the machine, but popular items do not expire from the cache.
- Tradução: Se sim, elementos de cache mensagem são previamente buscados antes que expirem para manter o cache atualizado. O padrão é não. Ligá-lo dá cerca de 10 por cento mais tráfego e carga na máquina , mas itens populares não expiram a partir do cache.
- Prefetch Key: <yes or no / sim ou não>
- If yes, fetch the DNSKEYs earlier in the validation process, when a DS record is encountered. This lowers the latency of requests. It does use a little more CPU.
- Tradução: Se sim, busca os DNSKEYs no início do processo de validação, quando um registro DS é encontrado. Isso diminui a latência de pedidos . Ele usa um pouco mais CPU.
Infra
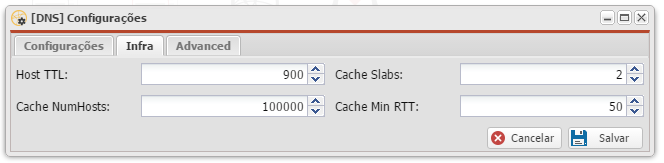
- Host TTL: <seconds / segundos>
- Time to live for entries in the host cache. The host cache contains roundtrip timing, lameness and EDNS support information. Default is 900.
- Tradução: Tempo de vida para as entradas no cache host. O cache de acolhimento contém ida e volta sincronismo, claudicação e EDNS informações de suporte. O padrão é 900 .
- Cache NumHosts: <number / número>
- Number of hosts for which information is cached. Default is 10000.
- Tradução: Número de hosts para os quais a informação é armazenada em cache . O padrão é 10000 .
- Cache Slabs: <number / número>
- Number of slabs in the infrastructure cache. Slabs reduce lock contention by threads. Must be set to a power of 2.
- Tradução: Número de lajes no cache de infra-estrutura. Lajes reduzir a contenção de bloqueio por threads. Deve ser definido como uma potência de 2 .
- Cache Min RTT: <msec / milissegundos>
- Lower limit for dynamic retransmit timeout calculation in infra-structure cache. Default is 50 milliseconds. Increase this value if using forwarders needing more time to do recursive name resolution.
- Tradução: limite inferior para o cálculo de retransmissão tempo limite dinâmica no cache de infra-estrutura. O padrão é 50 milissegundos . Aumente este valor se usando encaminhadores que necessitam de mais tempo para fazer a resolução de nomes recursiva.
Advanced
outgoing-range: <number> Number of ports to open. This number of file descriptors can be opened per thread. Must be at least 1. Default depends on compile options. Larger numbers need extra resources from the operating system. For performance a a very large value is best, use libevent to make this possible.
outgoing-port-permit: <port number or range> Permit unbound to open this port or range of ports for use to send queries. A larger number of permitted outgoing ports increases resilience against spoofing attempts. Make sure these ports are not needed by other daemons. By default only ports above 1024 that have not been assigned by IANA are used. Give a port number or a range of the form "low-high", without spaces. The outgoing-port-permit and outgoing-port-avoid statements are processed in the line order of the config file, adding the permitted ports and subtracting the avoided ports from the set of allowed ports. The processing starts with the non IANA allocated ports above 1024 in the set of allowed ports.
outgoing-port-avoid: <port number or range>
Do not permit unbound to open this port or range of ports for use to send queries. Use this to make sure unbound does not grab a port that another daemon needs. The port is avoided on all outgoing interfaces, both IP4 and IP6. By default only ports above 1024 that have not been assigned by IANA are used. Give a port number or a range of the form "low-high", without spaces.
outgoing-num-tcp: <number>
Number of outgoing TCP buffers to allocate per thread. Default is 10. If set to 0, or if do-tcp is "no", no TCP queries to authoritative servers are done. For larger installations increasing this value is a good idea.
incoming-num-tcp: <number>
Number of incoming TCP buffers to allocate per thread. Default is 10. If set to 0, or if do-tcp is "no", no TCP queries from clients are accepted. For larger installations increasing this value is a good idea.
so-rcvbuf: <number>
If not 0, then set the SO_RCVBUF socket option to get more buffer space on UDP port 53 incoming queries. So that short spikes on busy servers do not drop packets (see counter in netstatsu). Default is 0 (use system value). Otherwise, the number of bytes to ask for, try "4m" on a busy server. The OS caps it at a maximum, on linux unbound needs root permission to bypass the limit, or the admin can use sysctl net.core.rmem_max. On BSD change kern.ipc.maxsockbuf in /etc/sysctl.conf. On OpenBSD change header and recompile kernel. On Solaris ndd -set /dev/udp udp_max_buf 8388608.
so-sndbuf: <number>
If not 0, then set the SO_SNDBUF socket option to get more buffer space on UDP port 53 outgoing queries. This for very busy servers handles spikes in answer traffic, otherwise 'send: resource temporarily unavailable' can get logged, the buffer overrun is also visible by netstat -su. Default is 0 (use system value). Specify the number of bytes to ask for, try "4m" on a very busy server. The OS caps it at a maximum, on linux unbound needs root permission to bypass the limit, or the admin can use sysctl net.core.wmem_max. On BSD, Solaris changes are similar to so-rcvbuf.
so-reuseport: <yes or no>
If yes, then open dedicated listening sockets for incoming queries for each thread and try to set the SO_REUSEPORT socket option on each socket. May distribute incoming queries to threads more evenly. Default is no. On Linux it is supported in kernels >= 3.9. On other systems, FreeBSD, OSX it may also work. You can enable it (on any platform and kernel), it then attempts to open the port and passes the option if it was available at compile time, if that works it is used, if it fails, it
continues silently (unless verbosity 3) without the option.
